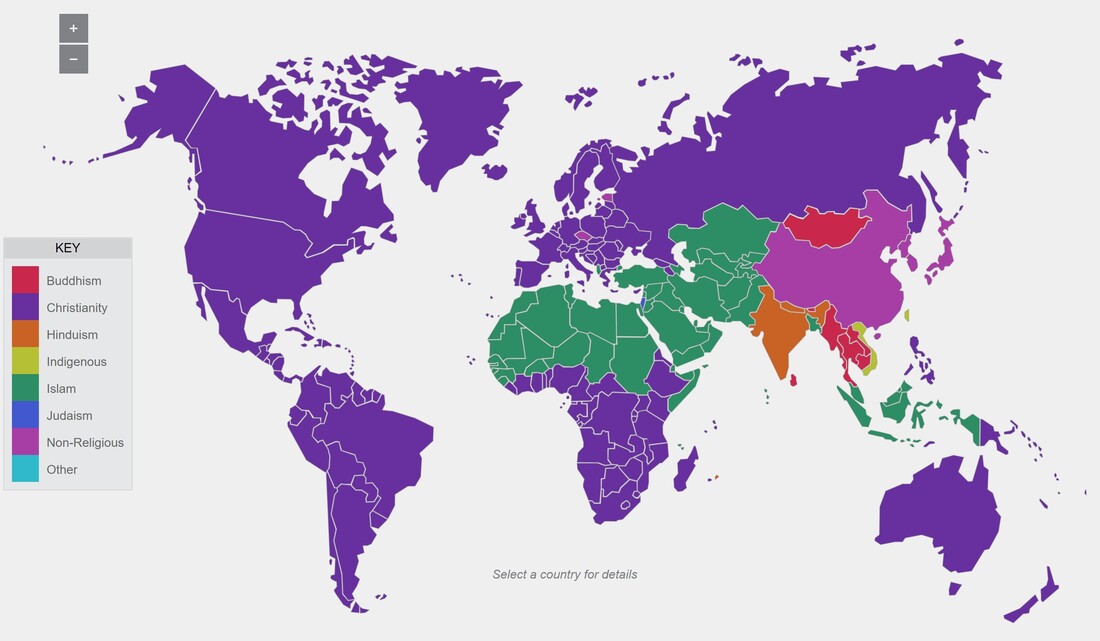
World Distribution Of Major Belief Systems
Find a world map colour in the map based on the worlds current Religious Affiliation. It is a complex but significant task to understand where different religious traditions are currently most prevalent.
Because of modern communications and the movement of people around the world, followers of all of these major belief systems may be found in the same city. Cultures and religions influence one another as they meet, and over a period of time their character may change and the relative influence in an area can change. Some examples of this:
- In much of Africa and South America, a number of the variants of Christianity exists alongside the traditional local tribal and animistic religions, also known as ethno-religions
- The three religions traditionally followed in China are Confucianism, Taoism and Buddhism and some Chinese may accept parts of all three, and the country is strongly influenced by Communism.
- In Japan, Shinto (the name given to the many traditional Japanese cults) is practised alongside Buddhism. There are a number of variants of Buddhism practised in Japan. As of December 2006, the Japanese Government recognized 154 schools of Buddhism includingTendai, Shingon, Jodo, Zen (Soto and Rinzai sects), Nichiren, and Narabukkyo.
| world_map.doc | |
| File Size: | 31 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
How many adherents are there?
|
Use the international tab of the ADRD site to develop responses to the following in a manner that can be presented.
Presentation of findings After the presentation of findings … Student write a brief response to the following
|
For your GLOSSARYAdherent
Variant Sect Denomination Conversion Invasion Genocide Migration Awakening |
Where did the religions come from?
|
Middle Eastern Religions:
Christianity (Palestine)
Zoroastrianism (Iran) Far Eastern (Asian) Religions:
Indian Religions:
African Religions:
American Religions:
Oceanic Religions:
|
|
|
|